Small businesses are an important part of the American economy and play a vital role in creating jobs and driving economic growth.
The history of small business in America is rooted in the country’s founding principles of individual liberty and economic freedom. America has always been a nation of entrepreneurs, with a long tradition of small business ownership dating back to colonial times.
During the colonial period, small businesses were primarily engaged in agriculture and craftsmanship. Many small farmers and artisans provided goods and services to their local communities, and their success was largely dependent on their ability to meet the needs of their customers.
In the 19th century, the growth of industry and technology led to the rise of small businesses in the manufacturing and retail sectors. The country’s expanding transportation network, including the railroad and the telegraph, also made it easier for small businesses to reach new markets.
In the 20th century, small businesses continued to play a vital role in the American economy. The post-World War II period saw a boom in small business ownership, as returning veterans started their own businesses and many women entered the workforce.
In recent decades, technology has enabled small businesses to expand their reach and increase their competitiveness. The internet, mobile technologies, and social media have made it easier for small businesses to connect with customers and compete with larger companies.
Small Businesses in America
Here are some statistics on small businesses in America as of 2021:
According to the Small Business Administration (SBA), small businesses make up 99.9% of all U.S. businesses and employ nearly half of all private sector workers.
Small businesses have created around 2 out of 3 new jobs in the U.S. in the last 15 years.
In 2020, there were 30.7 million small businesses in the United States, according to the SBA.
Small businesses with fewer than 500 employees make up 89% of all businesses.
Small businesses also account for 44% of U.S. economic activity.
The retail trade, accommodation and food services, and professional, scientific and technical services are among the sectors with the most small businesses.
Small businesses also account for a significant portion of the country’s exports, with small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) accounting for about one-third of the value of all U.S. exports.
Small Business After 2020
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on small businesses in 2020 and beyond. Many small businesses were forced to close their doors or significantly reduce their operations due to government-mandated lockdowns and social distancing measures. As a result, many small businesses have struggled to survive, and some have gone out of business.
However, some small businesses have adapted and found new ways to operate in the current environment. For example, many restaurants and retailers have turned to online sales and delivery services, while others have found new ways to provide services remotely.
The government has also provided various forms of aid to help small businesses survive the pandemic, such as the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) and the Economic Injury Disaster Loan (EIDL) program.
In addition, many small businesses have pivoted to new products or services to meet the changing demand of their customers.
Despite the challenges, many small businesses have shown resilience and have been able to survive the pandemic. However, the road to recovery will be long and difficult for many small businesses, and it will depend on the ability of the economy to recover and the evolution of the pandemic.
It’s worth noting that many small businesses are still facing financial difficulties and the future of many of them is uncertain. The government and society should continue to support small businesses with various forms of aid and policies to help them recover and thrive in the post-pandemic era.
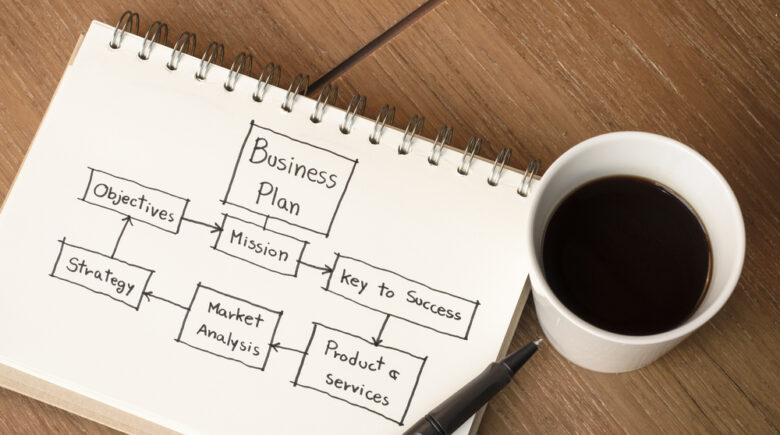
The Importance of Creating a Business Plan
Creating a business plan is an important step for entrepreneurs and small business owners. A business plan is a document that outlines the goals, strategies, and financial projections for a business. It serves as a roadmap for the future and helps entrepreneurs and small business owners to make informed decisions about their business.
Here are some reasons why creating a business plan is important:
- Helps to define the business: A business plan forces entrepreneurs and small business owners to think critically about their business and to clearly define their product or service, target market, and competitive advantage.
- Helps to identify potential challenges: A business plan helps entrepreneurs and small business owners to identify potential challenges and to develop strategies to overcome them.
- Helps to secure funding: A well-written business plan can help entrepreneurs and small business owners to secure funding from investors, banks, and other lenders.
- Helps to measure progress: A business plan serves as a benchmark for entrepreneurs and small business owners to measure progress and to make adjustments as needed.
- Helps to attract partners, employees and investors: A business plan is a powerful tool for attracting partners, employees, and investors.
- Helps to stay focused on the goal: A business plan helps entrepreneurs and small business owners to stay focused on their goals and to stay motivated throughout the journey.
In summary, creating a business plan is an important step for entrepreneurs and small business owners. It helps to define the business, identify potential challenges, secure funding, measure progress, attract partners, employees and investors, and stay focused on the goal.
How to Create a Business Plan
Creating a business plan is a key step for entrepreneurs and small business owners, as it helps to define the business, identify potential challenges, and secure funding. Here are some steps you can take to create a business plan:
- Research: Before you start writing your business plan, research your market, competition, and industry trends. This will help you to understand the opportunities and challenges that your business will face.
- Define your business: Clearly define your business, including the product or service you will offer, your target market, and your competitive advantage.
- Develop your marketing strategy: Develop a marketing strategy that outlines how you will reach your target market and how you will differentiate your product or service from your competition.
- Create financial projections: Create financial projections that outline your expected income, expenses, and profits for the next three to five years.
- Write the plan: Write the plan, using a clear and concise language. Include an executive summary, an overview of the business, the market, the product or service, the management team, the marketing and sales strategy, the financial projections, and an appendix with supporting documents.
- Review and revise: Review and revise your plan, making sure that it is clear, concise, and well-organized. Have someone else review it as well, to get a fresh perspective.
- Use it as a guide: Once your plan is complete, use it as a guide to help you make decisions, measure progress, and secure funding.
It’s worth noting that a business plan is a living document and should be reviewed and updated regularly as your business evolves. Additionally, the format and content of a business plan can vary depending on the business, the industry, and the purpose of the plan.